Blog
Blog

Good practices and technology for sustainable pig production
05th June 2025 - News
The Spanish pig farming sector has undergone a remarkable transformation in recent decades, establishing itself as one of the fundamental pillars of our country’s agri-food economy. However, this growth has brought with it significant environmental challenges, particularly regarding slurry management and pollutant emissions. In response, the sector has adopted a proactive approach, implementing practices and technologies aimed at minimizing its ecological footprint and promoting more sustainable production.
Sustainable slurry management
Slurry, a mixture of pig manure and urine, represents one of the main environmental challenges in the sector. Improper management can lead to soil and water contamination, as well as the emission of harmful gases such as ammonia.
To address this issue, various strategies have been developed, focusing on the recovery and proper treatment of these waste products. Among the most notable practices are:
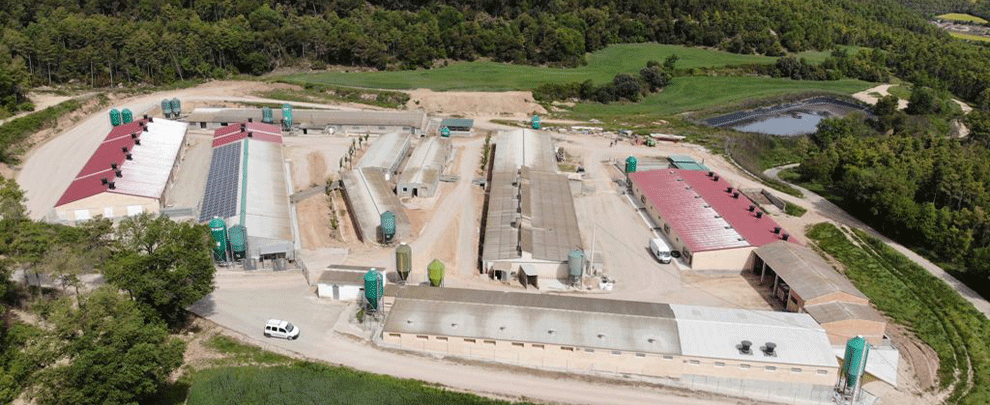
- Solid-liquid separation: This process divides the slurry into a solid fraction rich in organic matter and phosphorus, and a liquid fraction high in ammoniacal nitrogen. This separation allows for more efficient management, tailoring its agricultural application to the specific needs of the land and reducing the risk of runoff or leaching pollution.
- Slurry acidification: This technique involves lowering the slurry's pH, which reduces ammonia volatilization and, consequently, emissions into the environment. It also enhances slurry efficiency as a fertilizer by preserving nitrogen content more effectively.
- Biological treatment: By introducing specific bacteria, the decomposition of organic matter is promoted, reducing odors and improving slurry quality as a fertilizer.
- Band application: This slurry spreading technique minimizes exposure to air, significantly reducing ammonia emissions compared to traditional methods like broadcasting.
These practices not only help protect the environment but also offer economic benefits by improving nutrient use efficiency and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.

Slurry separation facilitates the management of this livestock byproduct. Photo: Rotecna.
Implementation of Best Available Techniques (BAT)
The adoption of Best Available Techniques (BAT) has become a key tool for the sustainability of the pig sector. These techniques, defined in the Implementing Decision (EU) 2017/302, aim to reduce pollutant emissions and improve resource use efficiency.
In Spain, Royal Decree 306/2020 establishes the mandatory implementation of BAT in intensive pig farms with a capacity exceeding 120 Livestock Units (LU). Among the most relevant BAT are:
- Multiphase low-protein feeding: Adjusting animal diets according to growth stages reduces nitrogen excretion, thereby lowering ammonia emissions.
- Frequent slurry removal: Regular emptying of slurry pits minimizes the production of polluting gases.
- Covering storage ponds: Preventing slurry from direct air exposure significantly reduces gas emissions.
According to the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food, 75% of pig farms have implemented these techniques, demonstrating the sector's commitment to sustainability.
Technological innovation for sustainability
Technology plays a crucial role in the sustainable transformation of the pig farming sector. The implementation of advanced monitoring and control systems enables more efficient resource management and a significant reduction in environmental impact.
Among the most prominent innovations are:
- Efficient ventilation and climate control systems: These improve animal welfare and reduce energy consumption.
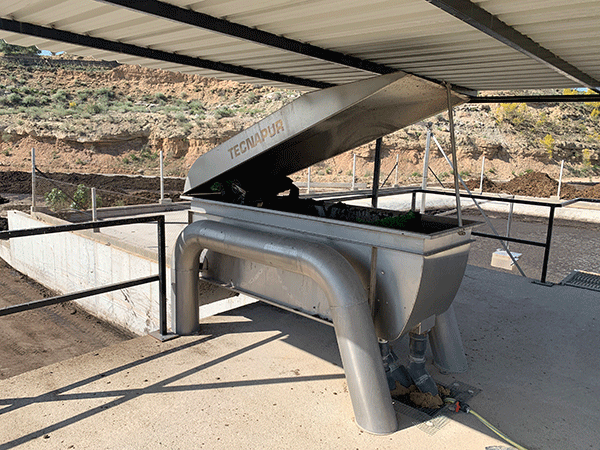
- Sensors and management platforms: These enable real-time monitoring of key parameters such as temperature, humidity, and air quality, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Waste treatment technologies: Processes like anaerobic digestion and phase separation contribute to more sustainable slurry management.
These tools not only optimize production but also reinforce the sector's commitment to environmental protection.
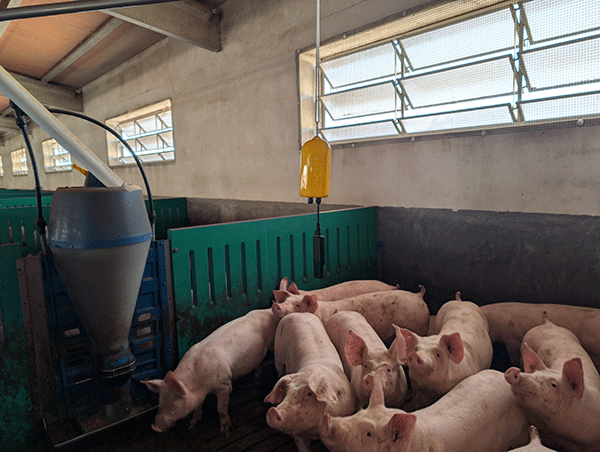

Sensors enable real-time monitoring of key parameters. Photo: Rotecna.
Communication and public perception
The public perception of the pig farming sector has often been shaped by environmental concerns. However, it is essential to highlight the efforts and progress made in terms of sustainability.
Transparent communication based on objective data is essential to inform the public about the responsible practices adopted by the sector. This includes sharing reports on BAT implementation, emission reductions, and technological innovations applied on farms.
Moreover, encouraging dialogue among producers, authorities, and civil society can contribute to a more balanced and fair understanding of the pig sector's role in the economy and the environment.
New challenges, new solutions
Sustainability in pig farming is not a destination but an ongoing process. As new regulations are developed, social expectations become more demanding, and scientific knowledge advances, opportunities arise to improve every link in the production chain.
The challenge now is to continue integrating solutions that combine technical efficiency, economic viability, and environmental responsibility. Optimizing water use, reducing the carbon footprint, and managing energy more effectively are among the next challenges the sector is already tackling.